Stock Market Investment
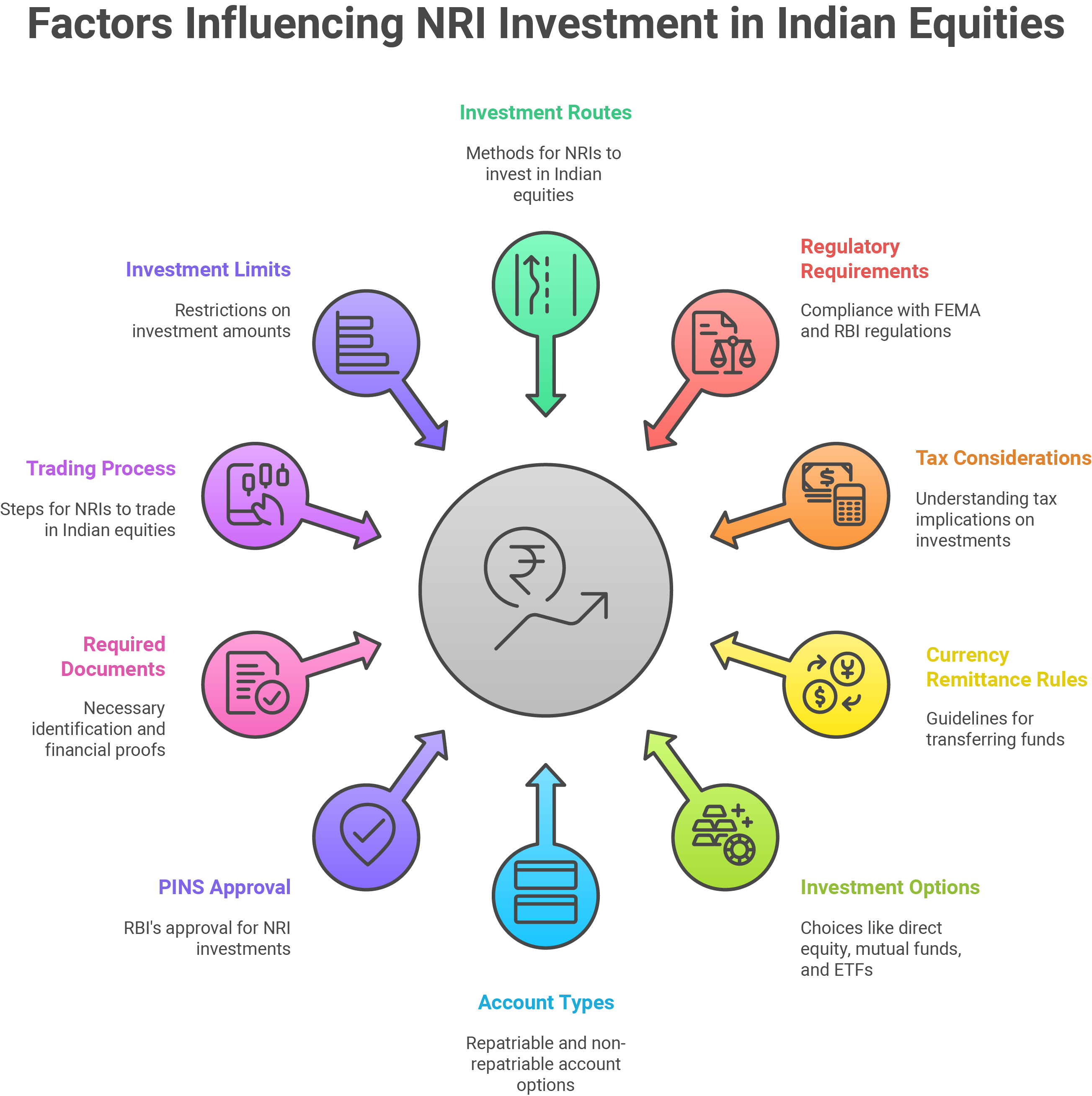
India’s dynamic stock market offers NRIs a powerful way to participate in the country’s economic growth and build long-term wealth. With access to equity shares, mutual funds, ETFs, and derivatives, NRIs can invest through regulated routes like the Portfolio Investment Scheme (PIS) or on a non-PIS basis via NRO accounts. However, investing in India also comes with regulatory requirements under FEMA and RBI, tax considerations, and currency remittance rules. This guide helps you understand the process, choose the right route, and invest confidently and compliantly in Indian equities.
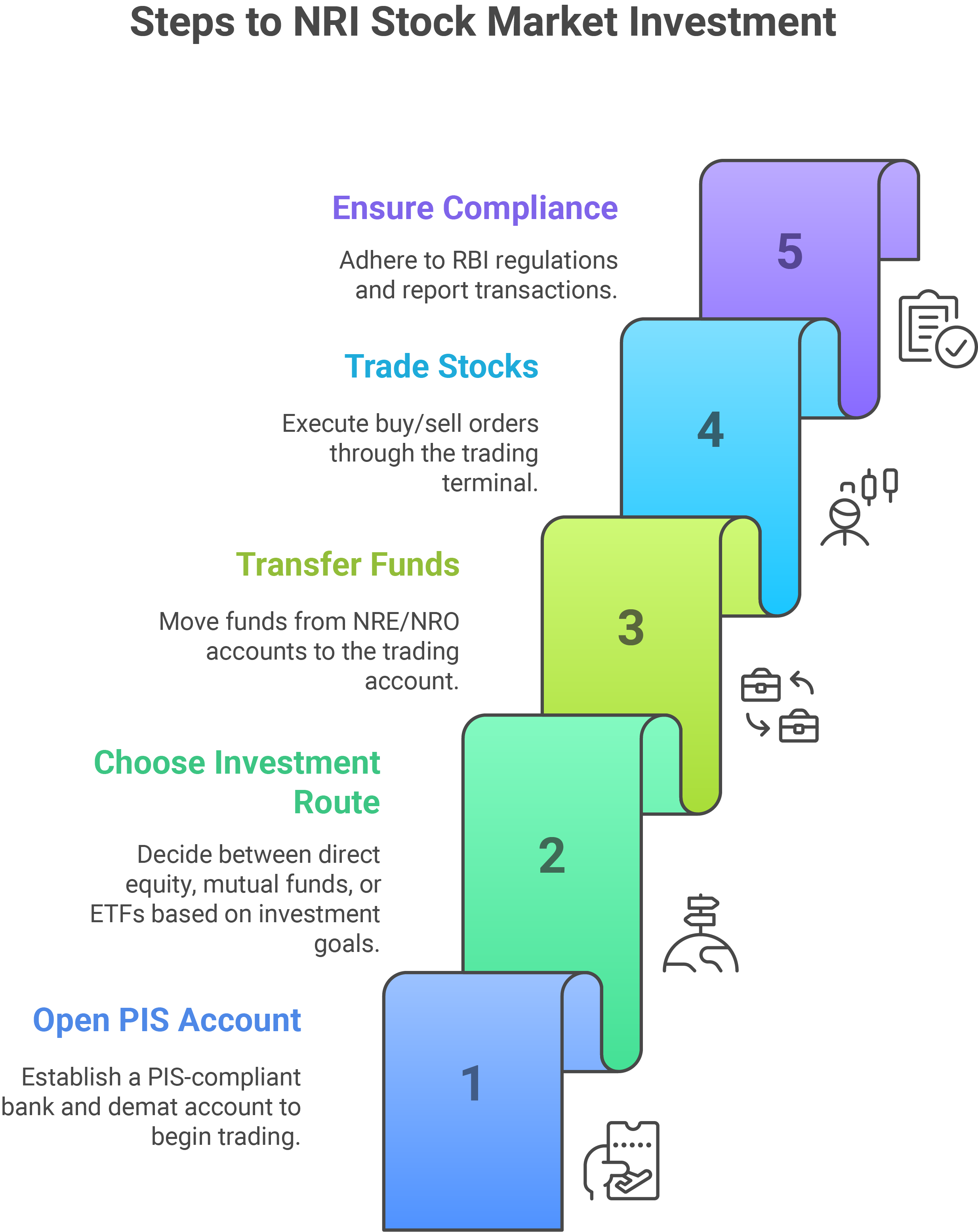
How to Invest in the Indian Stock Market by NRIs?
An NRI can depict investment in Indian stock markets by opening a PIS-compliant bank account with a demat account. Through these accounts, NRIs can make direct investments in equities or choose mutual funds. Even websites allow subscriptions to Initial Public Offerings, after which one can buy the shares of companies before those hit the secondary market.
Streamlined processes further allow NRIs to trade shares on the BSE and NSE, thereby developing a portfolio suited to their goals of investment.
Three Ways NRIs Can Invest in Indian Equities
NRIs can invest in Indian equities through the following methods:
- Direct Equity Investment: Under the PIS account, an NRI can directly invest in individual shares listed on Indian Exchanges. By doing so, they can have a diversified stock portfolio. This alternative will work for those who want hands-on investment in particular companies or sectors.
- Investment through Mutual Funds: These are managed funds whose portfolios comprise a mix of equities and bonds. Mutual Funds investment is an easy way for NRIs to invest without the need to select individual stocks. For the investors, the option to choose equity, debt, or hybrid funds based on the risk appetite that best fits makes mutual funds stand out as an attractive diversified exposure.
- Exchange-Traded Funds:They combine the features of both stocks and mutual funds, offering liquidity and diversification. For NRIs, ETFs offer diversified, cost-effective investing in a particular index, sector, or commodity with flexibility and lower transaction costs.
NRIs May Invest on Repatriable or Non-Repatriable Basis
NRIs may invest on either a repatriable or a non-repatriable basis, depending upon their objectives:
- Repatriable Investments: The investments made through its account are fully repatriable, meaning the principal and return are payable abroad. It is a go-to option for those NRIs who seek flexibility in drawing funds out from India internationally.
- Non-Repatriable Investments: The investments through an NRO account are non-repatriable beyond the limit, meaning thereby that such investments stay in India. This is suited for NRIs who plan to keep funds within the country for future needs.
What is PINS Approval from RBI?
Portfolio Investment Scheme (PINS) approval from the RBI is Rs. 10 lakh or $2,500 for NRIs dealing in Indian equities. This gives assurance that the investments by NRIs are tracked and put under scrutiny. Banks report every transaction through PINS to the RBI to show the transparency of transactions and adherence to Indian investment laws. PINS approval enables NRIs to trade confidently in Indian stocks within the ambit of regulatorily acceptable norms.
Documents Required for Opening
Trading cum Demat Account Documents required by an NRI to open a trading and demat account are as follows:
- Identification Proof: Passport, visa, and proof of overseas address.
- PIS Approval Letter: The letter will be issued by the bank in which the PIS account is maintained.
- PAN Card: This is required in paying one’s taxes in India.
- Bank Account Details: NRE or NRO account linked to the PIS account.
These may further be supplemented with additional KYC documents depending upon the demand by the brokers. It is always better to ensure that the NRIs have all the required documents to open the account before proceeding with the process.
How NRIs Actually Undertake the Trading Process
The following is the trading process of NRIs:
- Step 1: Transferring funds to the trading account from the NRE or NRO account.
- Step 2: Trade and investment dealing: chose stock through the trading terminal and issued buy/sell transaction orders to BSE or NSE.
- Step 3: The broker will prepare a PIS report for the RBI mentioning every single trade, basically to conserve the rules and regulations.
This will allow the NRIs to safely purchase and sell stock in a way that is considered compliant with Indian financial regulations.
Key Aspects NRIs Must Remember While Trading Indian Equities
- Investment Ceiling: NRI cannot invest more than 10% of paid-up the capital of the company.
- Tax Implications: These apply to dividends and capital gains; double taxation may apply unless there are treaties with the country of which the NRI is a citizen.
- Trading Restrictions: NRIs are only allowed delivery-based trading, hence they are not permitted for intraday trading.
All these aspects will help the NRIs in keeping their investments compliant and well-managed.
List of restricted stocks for the NRI-PIS account can be found by visiting the following websites:
- RBI: rbi.org.in/scripts/BS_FiiUSer.aspx
- NSDL: rbi.org.in/scripts/BS_FiiUSer.aspx
- CDSL: cdslindia.com/publications/FIMonitoring
Popular Demat & Trading websites in India include:
- SBI Bank – https://www.sbisecurities.in
- ICICI Bank – https://www.icicidirect.com/
- HDFC Bank – https://www.hdfcsec.com/
- Kotal Mahindra Bank – https://www.kotaksecurities.com/
- Axis Bank – https://simplehai.axisdirect.in/
- Motilal Oswal – https://www.motilaloswal.com/
- Anand Rathi – https://anandrathi.com/
- Sharekhan – https://www.sharekhan.com/
- Geojit Financials – https://www.geojit.com/
- Zerodha – https://zerodha.com/
Stock Market Investment FAQs
Answers to common NRI queries about stock market investments.